CE IVD
General
In-Vitro Diagnostic Medical Device Directive (98/79/EC) was established on December 7th, 1998. Three years and six months of grace were given from June 2000 and the directive became effective on December 7th, 2003 to all IVD devices until now.
In Vitro Diagnostic medical devices, or IVD's are critical medical devices that can be used to help the patient, physician and caregiver in reaching medical decisions. Their growing influence and added value in the worldwide medical device market, especially in the developing world become bigger. Technologically advanced development and automation can make IVD tests easier to use, more accurate, and able to give more timely results.
For in vitro diagnostic medical devices Directive 98/79/EC is a legal requirement for all manufacturers placing their products on the market in the EU, European Free Trade Area (EFTA), Switzerland, Turkey and some other countries wishing to join the EU.
The certification options under this IVD directive include Annex III, IV and VII comprising site audits and assessment of technical documentation. Our auditors who are nominated by notified bodies can do site audits and it will assess compliance to both EN ISO 13485:2003 and directive 98/79/EC together.
Applicable Products
List A
Reagents and reagent products, including related calibrators and control materials, for determining the following blood groups;
· ABO system
· RH (C, c, D, E, e)
· Anti-Kell blood type
· Reagents and reagent products, including related calibrators and control materials, for the detection, confirma tion and quantification in human specimens of markers of;
· HTLV I and II
· hepatitis B, C and D
List B
· Reagents and reagent products, including related calibrators and control materials, for determining the follow ing blood groups: anti-Duffy and anti-Kidd
· Reagents and reagent products, including related calibrators and control materials, for determining irregular anti-erythrocytic antibodies
· Reagents and reagent products, including related calibrators and control materials, for the detection and quanti fication in human samples of the following congenital infections: rubella, toxoplasmosis
· Reagents and reagent products, including related calibrators and control materials, for diagnosing the following hereditary disease: phenylketonuria
· Reagents and reagent products, including related calibrators and control materials, for determining the following human infections: cytomegalovirus, chlamydia
· Reagents and reagent products, including related calibrators and control materials, for determining the following HLA tissue groups: DR, A, B,
· Reagents and reagent products, including related calibrators and control materials, for determining the following tumoral marker: PSA
· Reagents and reagent products, including related calibrators, control materials and software, designed specifi cally for evaluating the risk of trisomy 21,
· The following device for self-diagnosis, including its related calibrators and control materials: device for the measurement of blood sugar
Self-test
· Annex III section 6. Design examination and legal manufacturer's declaration of conformity.
· Annex IV complete QAS and legal manufacturer's declaration of conformity.
· Annex V; test sample & documentation and EC type examination + Annex VI; batch product production and EC verification DoC.
· Annex V; test sample & documentation and EC type examination + Annex VII; production quality assurance and EC verification DoC.
In-vitro devices other than specific list A, B and self-test in Annex II.
· Annex III Quality assurance and legal manufacturer's declaration of conformity.
Scope of IVD
The IVD Directive is one of a suite of three directives which together cover all medical equipment. The associated directives are the Active Implantable Medical Devices Directive (AIMDD) and the Medical Devices Directive (MDD).
The Directive defines an IVD device as “any medical device which is a reagent, reagent product, calibrator, control material, kit, instrument, apparatus, equipment, or system, whether used alone or in combination, intended by the manufacturer to be used in vitro for the examination of specimens, including blood and tissue donations, derived from the human body, solely or principally for the purpose of providing information: concerning a physiological or pathological state, or concerning a congenital abnormality, or to determine the safety and compatibility with potential recipients, or to monitor therapeutic measures.“
This definition needs to be read in conjunction with the definition of a medical device in the Medical Devices Directive.
Examples of IVD
· Laboratory centrifuge, blood composition analyzer.
· Personal use OTC devices: blood sugar monitors, pregnancy testers.
· Specimen receptacles and other accessories to an IVD device are also considered as IVD devices
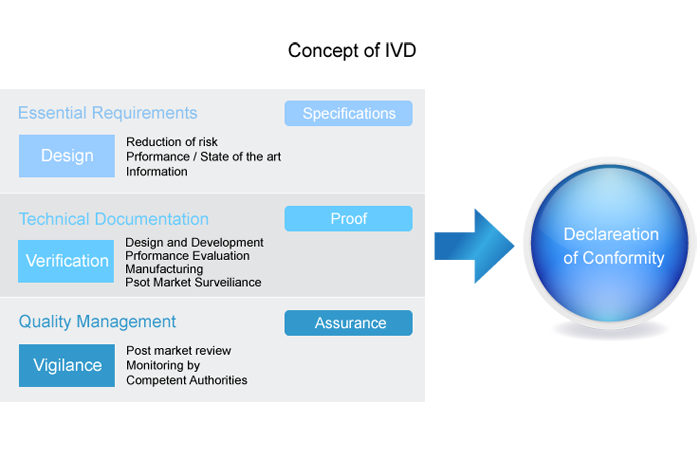
Essential Requirements of CE/IVD marking
The ‘manufacturer’ or authorized representative, as the legal entity in Europe, must ensure that the device meets the essential requirements specified in Annex I of the Directive and follow the appropriate conformity assessment procedure.
Administrative requirements
· Manufacturers (or their agents) must typically
· Comply with the essential requirements of annex 1 of the Directive
· Demonstrate design verification
· Carry out a risk assessment
· Demonstrate clinical evidence of the effectiveness of the device
· Implement a procedure for post market surveillance
· Complete a Declaration of Conformity
· Maintain a file of technical information about the product
· Put the CE mark on the product (or its packaging)
· For General Devices, register with the Medicines and Healthcare products regulatory Agency, the Competent Authority in EU member state or, for all other devices apply to a Notified Body.
Safety Requirements
· General requirement for safe design
· Minimization of risks from contamination
· Compatibility with materials with which they are likely to come into contact
· Minimization of hazards of infection and microbial contamination
· Provision of sufficient accuracy
· Protection against radiation
· Adequate product marking
· Adequate user instructions


